About CompTIA Certification Exams
CompTIA serves the IT industry as the world's largest developer of vendor-neutral IT certification exams. Since establishing the certification program in 1993, more than one million CompTIA certifications have been earned worldwide. Currently, CompTIA offers certifications in PC hardware, networking, servers, e-Business, convergence, project management, training, Linux, security, digital home technology, document imaging and RFID.
CompTIA A+ Certification
Earning CompTIA A+ certification proves that a candidate has the latest skills needed by today's computer support professionals. CompTIA A+ confirms a technician's ability to perform tasks such as installation, configuration, diagnosing, preventive maintenance and basic networking. The exams also cover domains such as security, safety and environmental issues and communication and professionalism.
CompTIA Network+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Network+ certification demonstrates that a candidate can describe the features and functions of networking components, and possesses the knowledge and skills needed to install, configure and troubleshoot basic networking hardware, protocols and services. The exam tests technical ability in the areas of media and topologies, protocols and standards, network implementation and network support.
CompTIA Security+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Security+ certification demonstrates proof of knowledge and expertise in security topics, such as communication security, infrastructure security, cryptography, access control, authentication, external attack and operational and organization security.
CompTIA RFID+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA RFID+ certification validates an RFID technician's knowledge and skills in the areas of installation, maintenance, repair, and upkeep of hardware and software functionality of RFID products.
CompTIA Server+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Server+ certification validates advanced-level technical competency of server issues and technology; including installation, configuration, upgrading, maintenance, environment, and troubleshooting and disaster recovery. This certification is intended for mid to upper-level technicians.
CompTIA e-Biz+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA e-Biz+ certification proves that a candidate knows the basic concepts, key issues and critical technologies of e-business. CompTIA e-Biz+ is designed for technical and non-technical individuals who work in an e-business environment. The exam is only available in Korean and Japanese languages.
CompTIA CTT+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA CTT+ certification proves excellence in preparation, presentation, communication, facilitation and evaluation in a classroom environment. CompTIA CTT+ is a two-part exam: computer-based and video-based.
CompTIA CDIA+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Certified Document Imaging Architech (CDIA+) certification validates expertise in the technologies and best practices used to plan, design, and specify a document imaging and management system.
CompTIA Linux+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Linux+ certification proves that a candidate can explain fundamental open source resources/licenses, demonstrate knowledge of user administration, understand file permissions/software configurations and manage local storage devices and network protocols.
CompTIA Project+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Project+ certification validates fundamental project management skills. It covers the entire project life cycle from initiation and planning through execution, acceptance, support and closure.
CompTIA Convergence+ Certification
Earning a CompTIA Convergence+ certification proves knowledge and skills in the area of Communications Technologies (CT), where datacomm, telephony/telecommunications, video and broadcast multimedia technologies combine into a single IP-based delivery system.
CEA-CompTIA DHTI+ Certification
Earning a CEA-CompTIA DHTI+ certification demonstrates that a candidate can configure, integrate, maintain, troubleshoot, and comprehend the basic design concepts of electronic and digital home systems.
CompTIA PDI+ Certification
CompTIA PDI+ certification proves that a candidate has the knowledge and skills to provide basic support for printing and document imaging devices. The exam covers domains such as print and scan processes and components, basic electromechanical tools, color theory as well as the soft skills of customer service and professionalism and safety and environment.
 Power users like keyboard shortcuts and commands to quickly access many things in Windows. They save lot of mouse clicks and time. In this post let us see how to quickly launch Control Panel Applets using Run Command window.
Power users like keyboard shortcuts and commands to quickly access many things in Windows. They save lot of mouse clicks and time. In this post let us see how to quickly launch Control Panel Applets using Run Command window.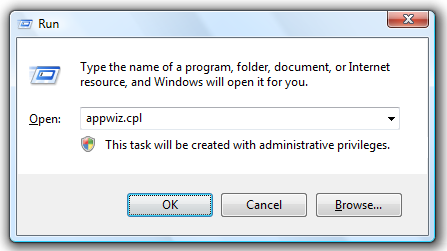

 The amount of garbage accumulated on the computer keeps growing as we install/uninstall applications, updates and browse the Internet. Few application un-installers does not remove all the files properly, application crashes leaves memory dumps, browsing Internet adds media files, cookies and other junk to cache folders. The garbage not only eats up our valuable Hard Disk space but also slows computer performance.
The amount of garbage accumulated on the computer keeps growing as we install/uninstall applications, updates and browse the Internet. Few application un-installers does not remove all the files properly, application crashes leaves memory dumps, browsing Internet adds media files, cookies and other junk to cache folders. The garbage not only eats up our valuable Hard Disk space but also slows computer performance.